The certification in accordance with DIN 8330
An examination in three categories with 16 individual tests
Test contents are focused on readability, operability, accuracy and power reserve of the watches.
In addition to tests in the fields of water resistance, G-load capacity, vibration, shock and impact resistance, this category also provides resistance to liquids typical of flight operations.
03. Safety and compatibility »
Test scenarios include magnetic signature, glare effects, compatibility with cockpit lighting or night vision devices and strap attachment.
Designed for professional wear - yet a must have for any pilot watch lover!
German DIN standards enjoy the highest reputation worldwide and are thus a decisive quality feature. The DIN 8330 standard for pilot watches sets the ultimate standard, for extremely reliable, functional, safe and tested pilot watches.
With the Hamburg Din 8330 and the Hamburg GTM Din 8330 we offer certified and aviation-approved pilot watches not only to professional users, but also to watch - enthuasiats with high-quality standards that go far beyond everyday suitability.
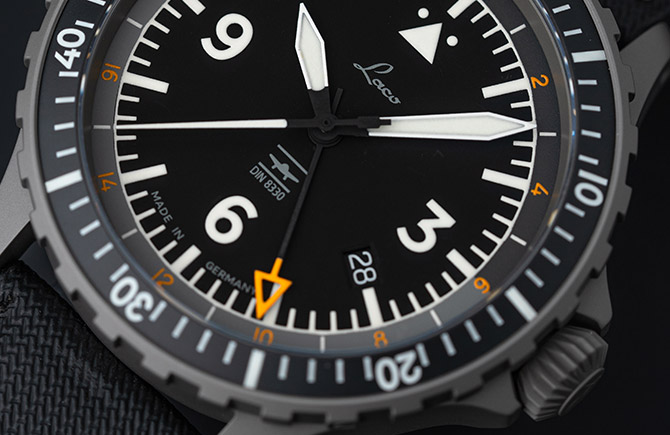

Functionality
01 Readability
DIN 8330 defines the stresses a Pilot watch must withstand and the performance it must provide. This includes for example the fast, clear and exact readability of the time, during the day and at night, as well as under difficult conditions such as strong vibrations.

Functionality
02 Usability
It must be possible to operate the watch even under difficult or extreme conditions. Din 8330 requires a proper operation with gloves.
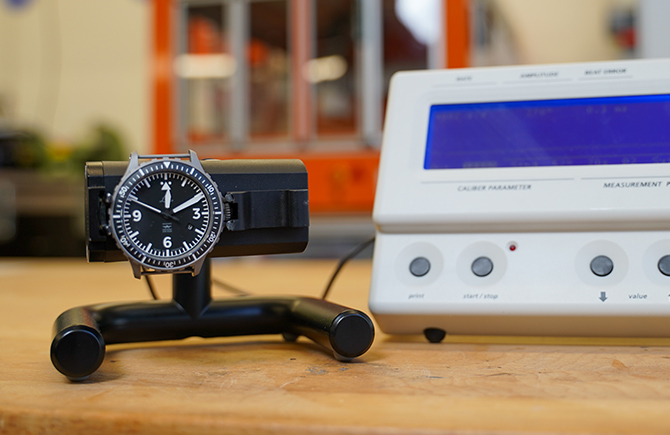

Functionality
03 Running accuracy
In order to assess the accuracy of the timekeeping, a timing machine is used. The watch is clamped into the timing machine in various positions. By means of an acoustic measurement of the movement, the time deviation of the watch (accuracy) is determined over a 24-hour period.

Functionality
04 Power reserve
In essence, the power reserve signifies the stored energy capacity of a mechanical watch - or more precisely, the duration for which the watch can continue to run. Just as with the timekeeping accuracy, the DIN 8330 standard mandates a rigorous assessment within the temperature range of -15°C and +55°C.
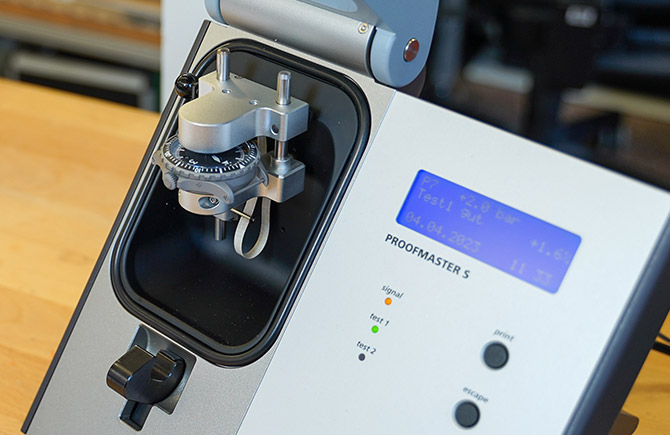

Resistance to external stresses
01 Water resistance
Water resistance is also of great importance in flight operations. Temperature and pressure differences favor the penetration of air humidity into the case and could lead to fogging of the watch glass.
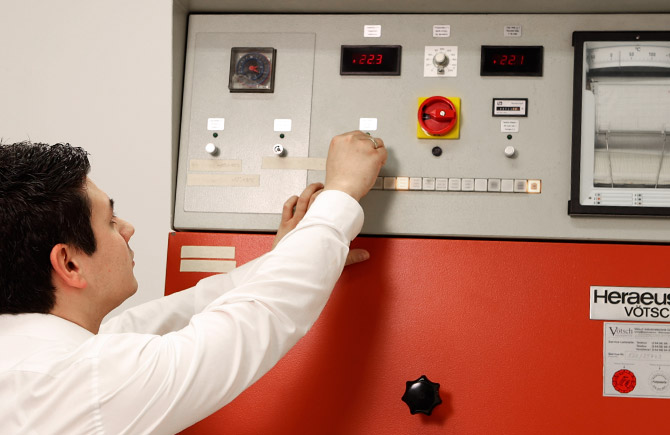

Resistance to external stresses
02 Temperature change
Aircraft are exposed not only to extreme forces, but also to extreme temperatures. These conditions not only challenge aircraft technology but also pilot watches. It's important for pilot watches to be able to withstand temperature fluctuations, as the movement contains various metals that have different coefficients of thermal expansion. In the worst case, these metals can expand or contract to the point where the movement is no longer functional. For that reason, pilot watches are subjected to thermal shock testing to ensure they can withstand the high rigors of flight operations.
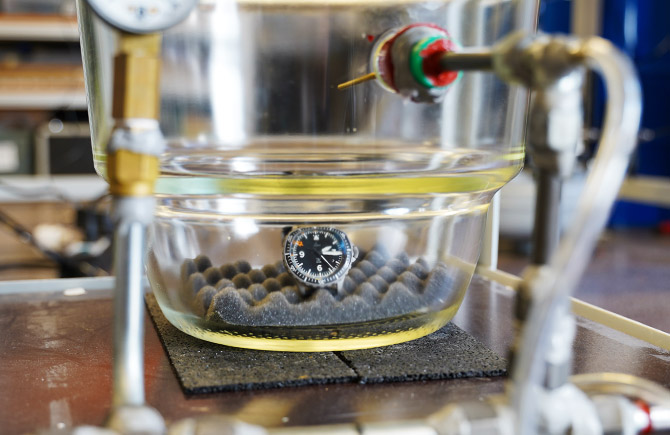
Resistance to external stresses
03 Environmental pressure
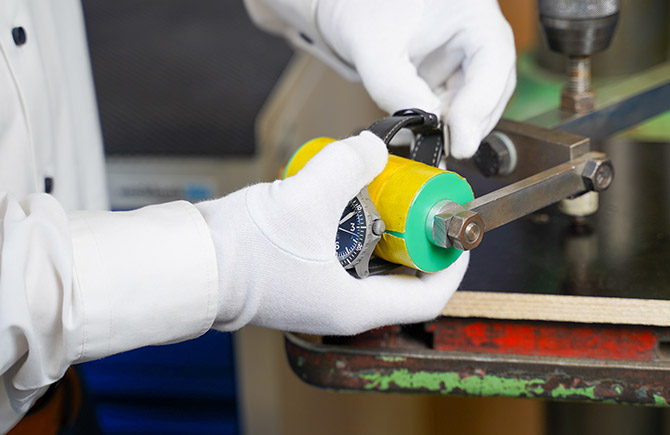
Aircraft can be subjected to loads that involve extreme pressure. The pilot's watch must also be able to withstand these pressures. For this reason, the watch is subjected to a pressure cycling test, because a drop in pressure can cause an abrupt overpressure in the case, which can cause the glass to pop out or mechanical components to jam.

Resistance to external stresses
04 G-load pressure
During flight operations, aircraft are sometimes subjected to high G-forces. The pilot's watch must also be able to resist these stresses. Especially in general flying, flight maneuvers can lead to higher g-accelerations, where the watch and especially the movement are also exposed to these G-forces. To ensure that pilot watches can stand up to these loads, they are subjected to a G-load test.

Resistance to external stresses
05 Vibrations
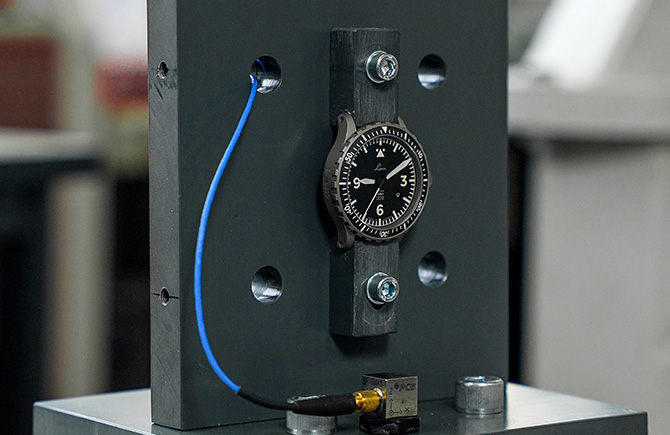
During flight operations, aircraft are not only exposed to high temperatures, pressures and G-forces, but also to vibrations that can lead to transient G-loads. These vibrations can have a significant effect on the pilot's watch and due to the change in amplitude, this can lead to impairments of the movement. If the natural frequency of the movement is hit, this may even lead to direct destruction of the movement. To check the stability of the watches against these vibrations, a vibration test is performed.

Resistance to external stresses
06 Impact and shock resistance
In this test, impacts on the watch or free-fall impacts are induced on specific positions. Because even weak impacts are enough to put the movement out of operation, several impacts are applied to a watch sample at a speed of approx. 4.5 m/s during this test.
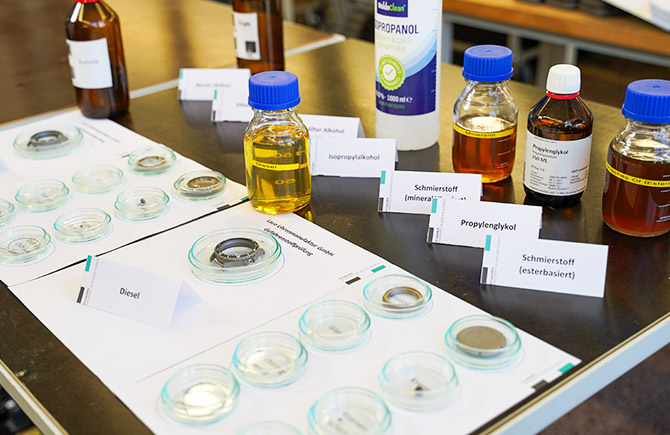

Resistance to external stresses
07 Resistance to liquids typical of flight operations
DIN 8330 is a norm that specifies the requirements for pilot watches. This standard states that pilot watches not only have to withstand the typical loads of flight operations, but also have to be chemically resistant. For this reason, the various components of the pilot's watch must also be exposed to fluids typical of flight operations in order to test their resistance. That's important because pilot watches frequently come into contact with liquids such as fuel, oil and other chemicals that can corrode the watch's material and affect its accuracy and reliability.

Resistance to external stresses
08 Magnet fields
Resistance to external loads according to DIN 8330 includes extremely high protection against magnetic or electromagnetic influences. Corresponding tests are carried out with the aid of a Helmholtz coil, among other things.
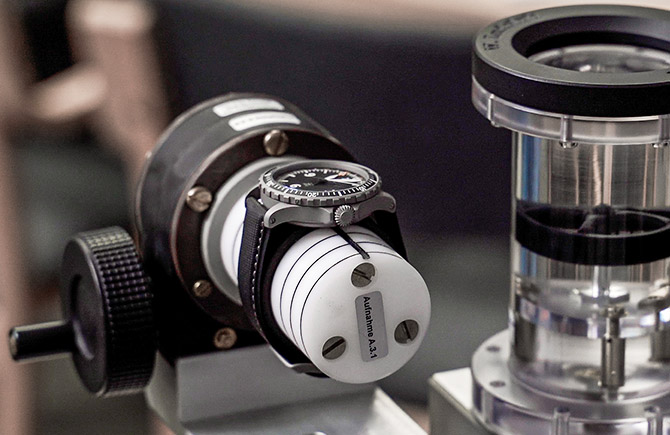

Safety and compatibility
01 Magnetic signature
The magnetic signature of a pilot's watch to DIN 8330 should not significantly interfere with the magnetic compasses approved in aircraft due to their close proximity. The test includes the measurement with the smallest possible distance that arises between the magnetic compass and the watch during the execution of all actions required in flight operations, even if this is only the case for a short time.

Safety and compatibility
02 Glare
Light reflections that could glare or distract the pilot are extremely well minimized in accordance with DIN 8330.

Safety and compatibility
03 Compatibility with cockpit lighting and night vision devices
The safety aspects of a pilot's watch that is certified in accordance to DIN 8330 are made particularly clear by its required compatibility with cockpit lighting and night vision equipment. Possible interference with the avionics is also prevented.

Safety and compatibility
04 Strap fastening
In an emergency, the watch and the strap can be subjected to much higher forces than in daily use, for instance. Compliance with the DIN 8330 standard entails subjecting the entire wristband system to extreme stresses during testing.
„Our DIN 8330 certified pilot watches are a milestone in our history and a testament to our unwavering dedication to quality, precision and innovation.“
Uwe Rücker, CEO Laco Uhrenmanufaktur










.png)
